14.2. dSPACE deployment through Simulink Coder¶
This process applies to the following dSPACE platforms
dSPACE MicroAutoBox II
dSPACE AutoBox
dSPACE MicroLabBox
Note
FORCESPRO currently does not support the dSPACE MicroAutoBox II platform. This example has remained as a guideline for deployment to other target platforms.
Important
When deploying to a target hardware platform, the library included in the lib_target directory of the generated solver should be used instead of the library in the lib directory.
14.2.1. Platform Specific Configurations¶
14.2.1.1. Platform name codeoption¶
When generating code for HW target platforms, codeoptions.platform needs to be set.
dSPACE MicroAutoBox II:
'dSPACE-MABII'dSPACE AutoBox:
'dSPACE-AutoBox'dSPACE MicroLabBox:
'dSPACE-MicroLabBox'
14.2.1.2. Simulink Model HW Target Configuration¶
When creating a Simulink Model for HW target platforms, certain hardware options need to be set.
Simulink Model Template:dSPACE MicroAutoBox II:
RTI1401dSPACE AutoBox:
RTI1007dSPACE MicroLabBox:
RTI1202
System target file:dSPACE MicroAutoBox II:
rti1401.tlcdSPACE AutoBox:
rti1007.tlcdSPACE MicroLabBox:
rti1202.tlc
Template makefile:dSPACE MicroAutoBox II:
rti1401.tmfdSPACE AutoBox:
rti1007.tmfdSPACE MicroLabBox:
rti1202.tmf
14.2.2. High-level interface¶
The steps to deploy and simulate a FORCESPRO controller on a dSPACE platform are detailed below.
(Figure 14.1) Set the code generation options (for
<platform_name>see Platform name codeoption):
codeoptions.platform = '<platform_name>'; % to specify the platform
codeoptions.printlevel = 0; % on some platforms printing is not supported
codeoptions.cleanup = 0; % to keep necessary files for target compile
and then generate the code for your solver (henceforth referred to as “FORCESNLPsolver”, placed in the folder “BasicExample”) using the high-level interface.
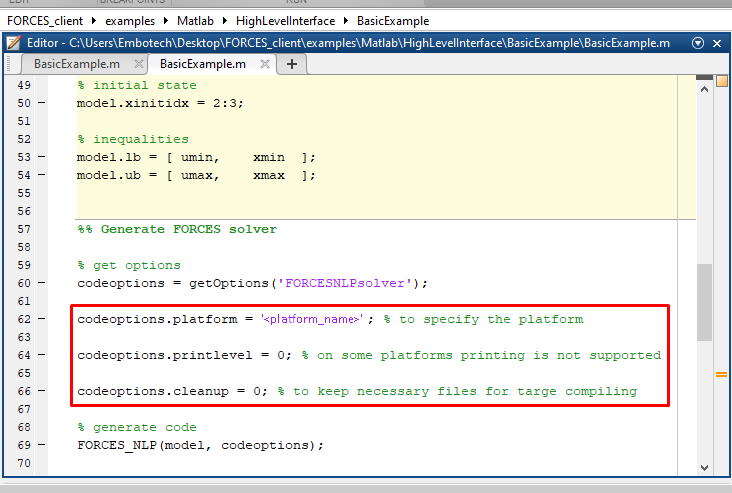
Figure 14.1 Set the appropriate code generation options.¶
(Figure 14.2) Create a new Simulink model using the Simulink model template provided by dSPACE (for
<simulink_model_template>see Simulink Model HW Target Configuration).(Figure 14.3) Populate the Simulink model with the system you want to control.
Figure 14.2 Create a Simulink model.¶
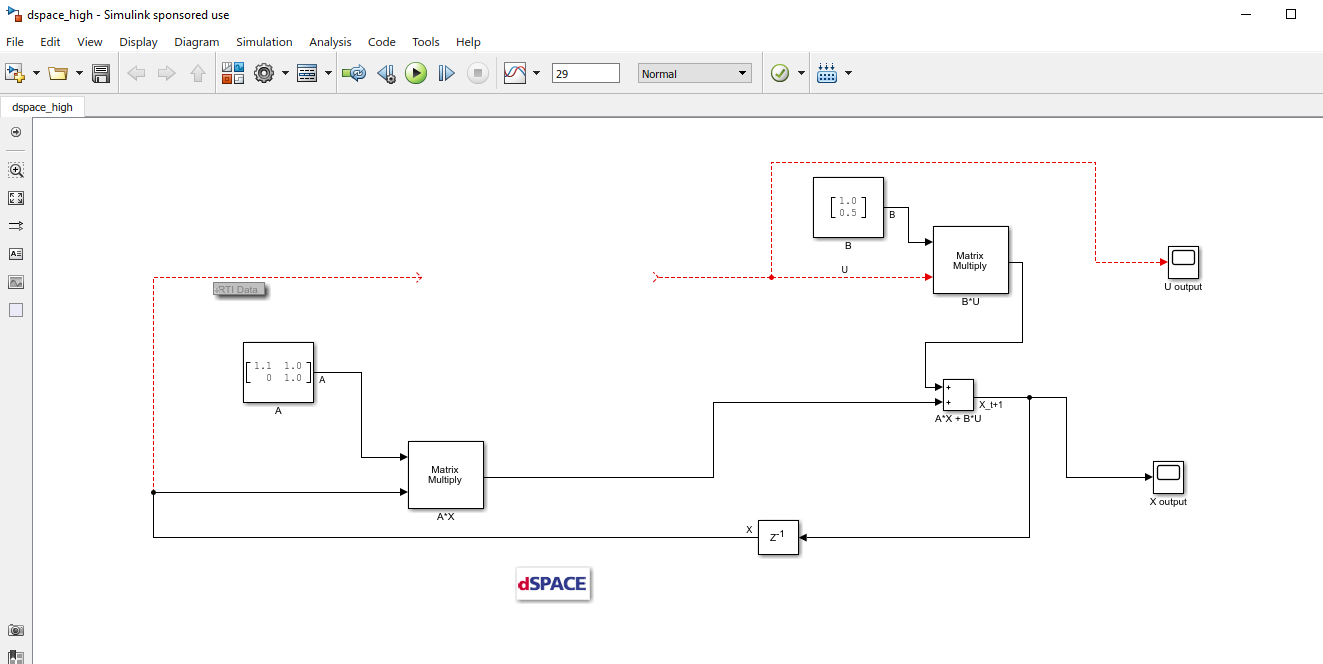
Figure 14.3 Populate the Simulink model.¶
(Figure 14.4) Make sure the
FORCESNLPsolver_simulinkBlock.mexw64file (created during code generation) is on the MATLAB path.
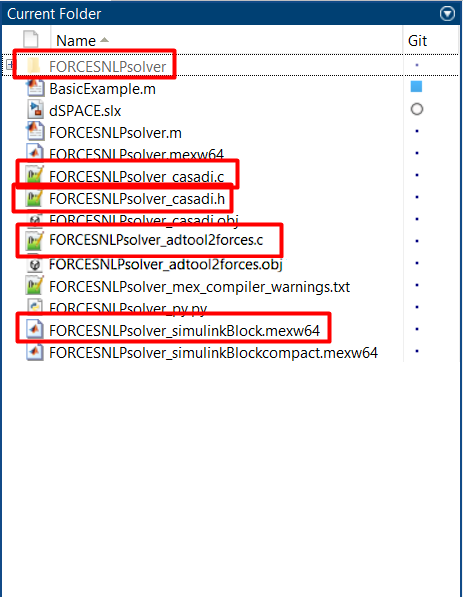
Figure 14.4 Add the folder containing the .mexw64 solver file to the MATLAB path.¶
(Figure 14.5) Open the
FORCESNLPsolver_lib.mdlSimulink model file, contained in theinterfacefolder of theFORCESNLPsolverfolder created during code generation.(Figure 14.6) Copy-paste the FORCESPRO Simulink block into your simulation model and connect its inputs and outputs appropriately.
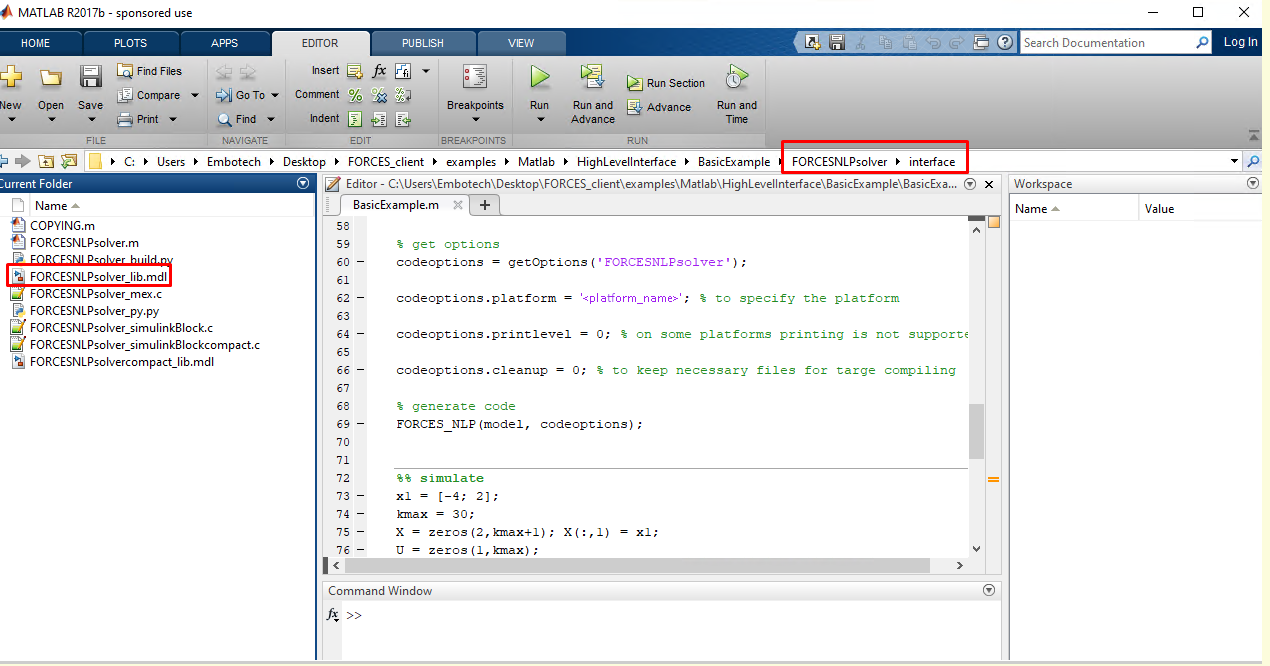
Figure 14.5 Open the generated Simulink solver model.¶
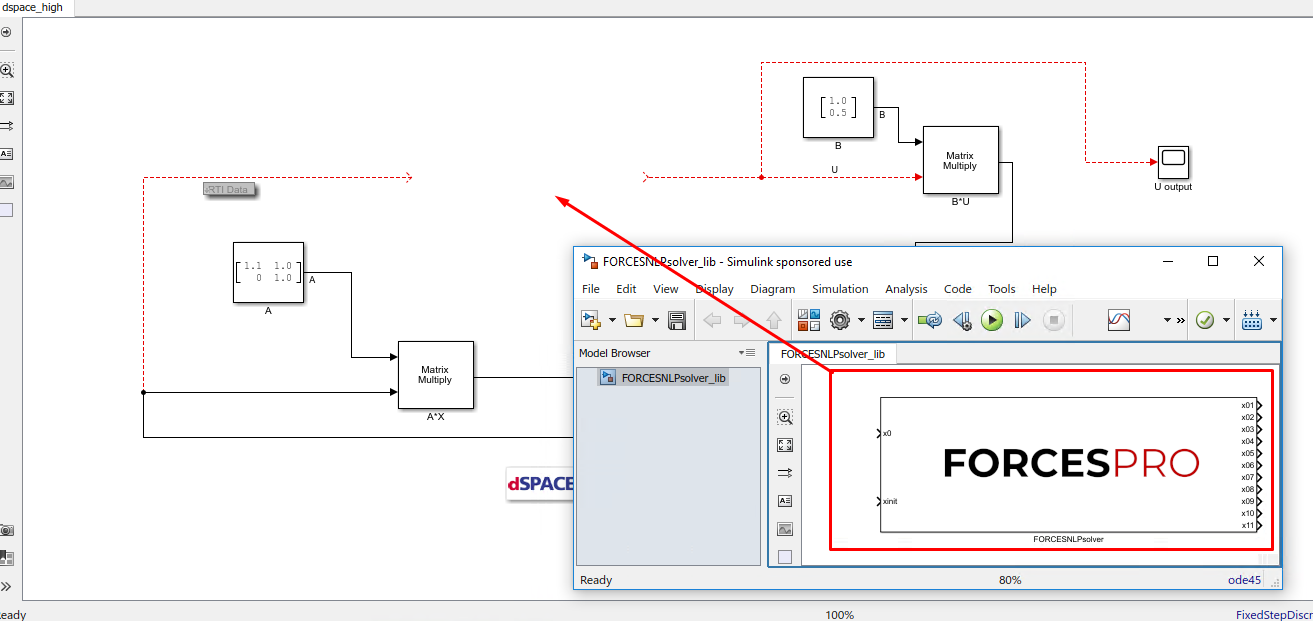
Figure 14.6 Copy-paste and connect the FORCESPRO block.¶
(Figure 14.7) Access the Simulink model’s options.
(Figure 14.8) In the “Solver” tab, set the options:
Simulation start/stop time: Depending on the simulation wanted.
Solver type: Discrete or fixed-step.
Fixed-step size: Needs to be higher than the execution time of the solver.
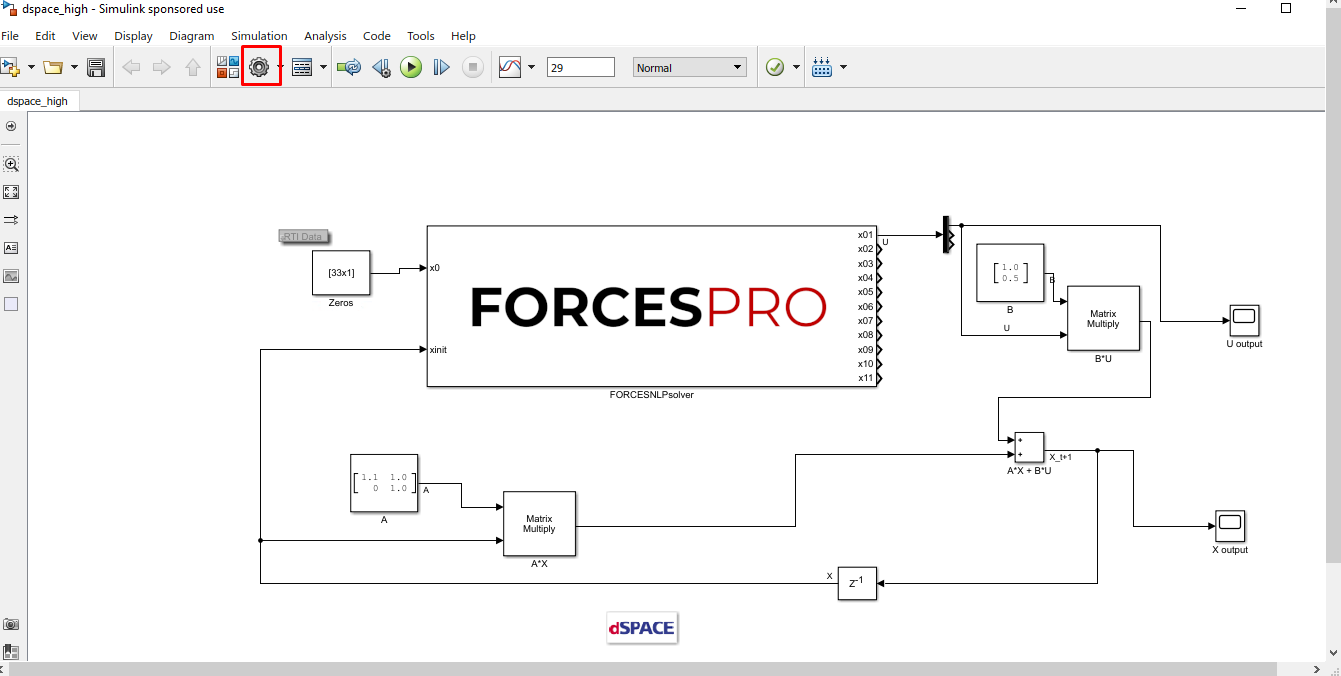
Figure 14.7 Open the Simulink model options.¶
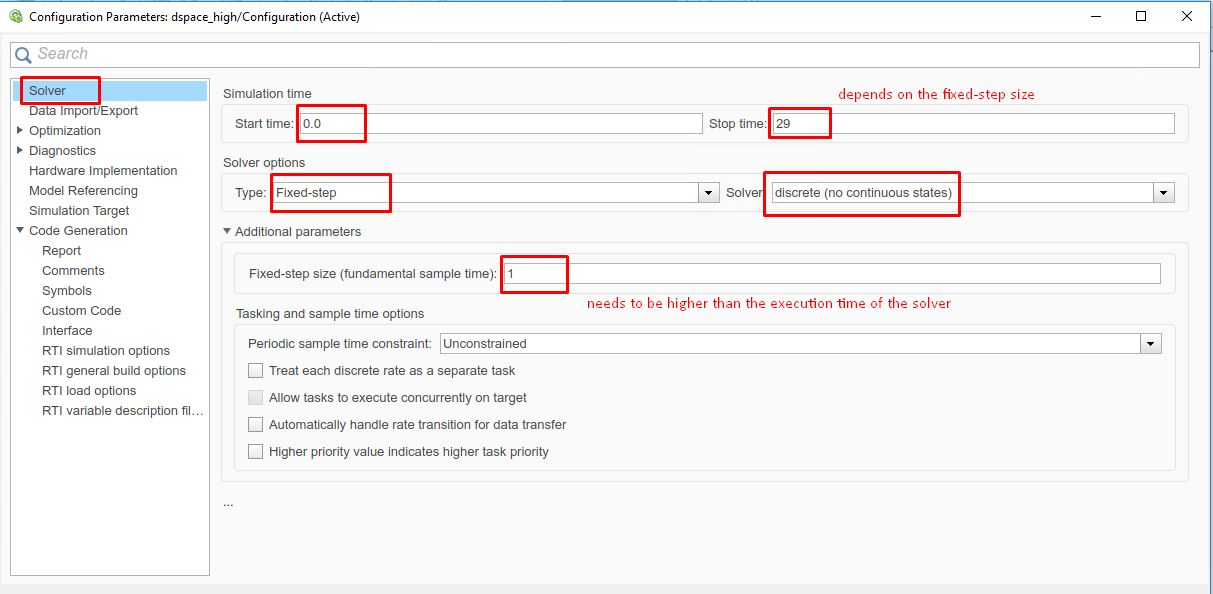
Figure 14.8 Set the Simulink solver options.¶
(Figure 14.9) In the “Code Generation” tab, set the options (for
<tlc_file>and<makefile_template>see Simulink Model HW Target Configuration):
System target file:
<tlc_file>Language: C
Generate makefile: On
Template makefile:
<makefile_template>Make command:
make_rti
(Figure 14.10) In the “Code Generation/Custom Code” tab, include the directories:
BasicExample
BasicExample\FORCESNLPsolver\interface
BasicExample\FORCESNLPsolver\lib_target
(Figure 14.11) In the “Code Generation/Custom Code” tab, add the source files:
FORCESNLPsolver_simulinkBlock.c
FORCESNLPsolver_adtool2forces.c
FORCESNLPsolver_casadi.c
(Figure 14.12) In the “Code Generation/Custom Code” tab, add the library file:
FORCESNLPsolver.lib
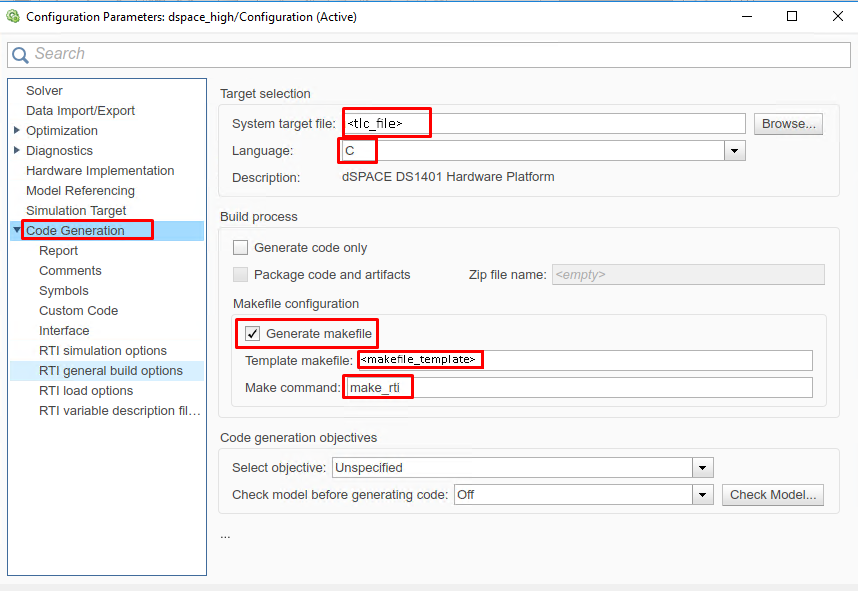
Figure 14.9 Set the Simulink code generation options.¶
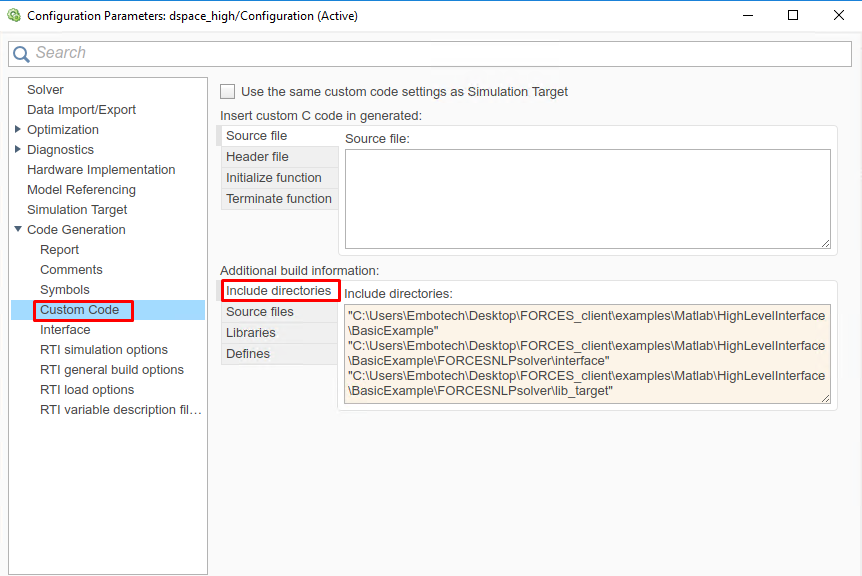
Figure 14.10 Add the directories included for the code generation.¶
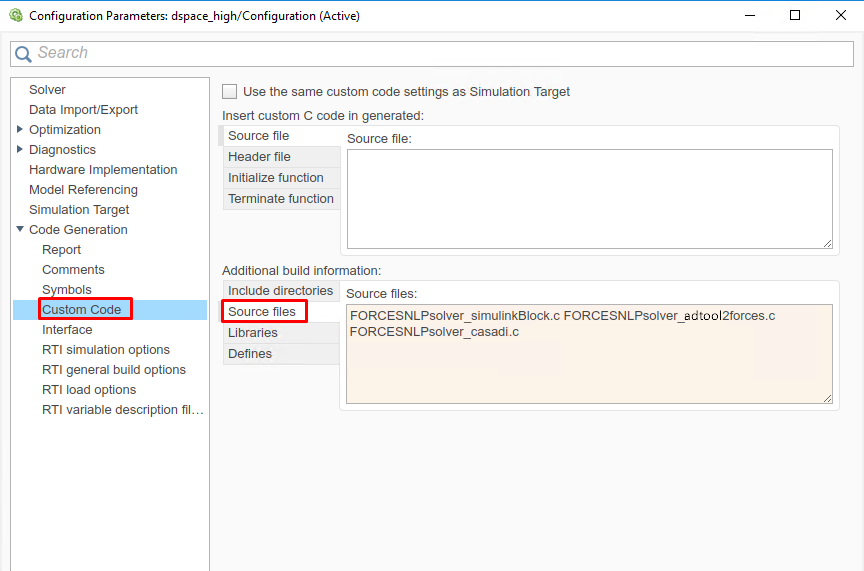
Figure 14.11 Add the source files used for the code generation.¶
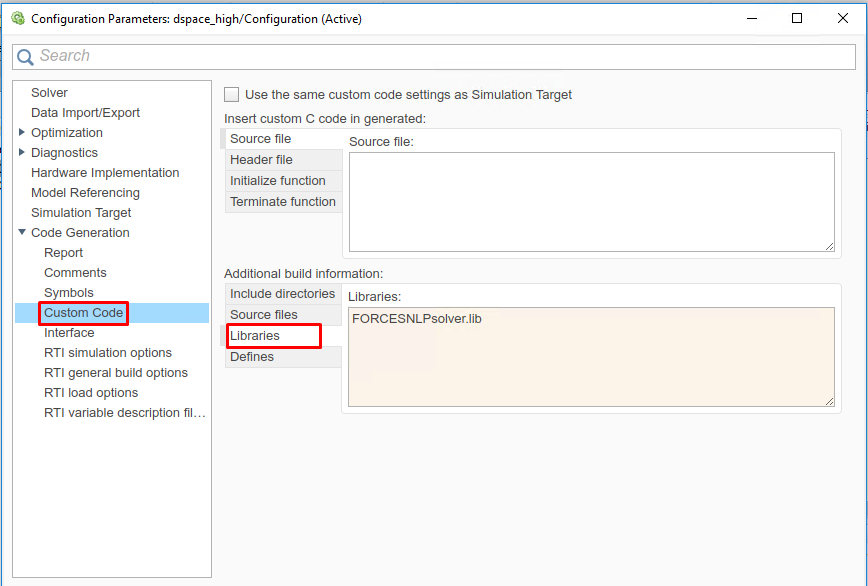
Figure 14.12 Add the libraries used for the code generation.¶
(Figure 14.13) Access the FORCESPRO block’s parameters.
(Figure 14.14) Remove the “FORCESNLPsolver” prefix from the S-function module.
(Figure 14.15) Compile the code of the Simulink model. This will also automatically load the model to the connected dSPACE platform.
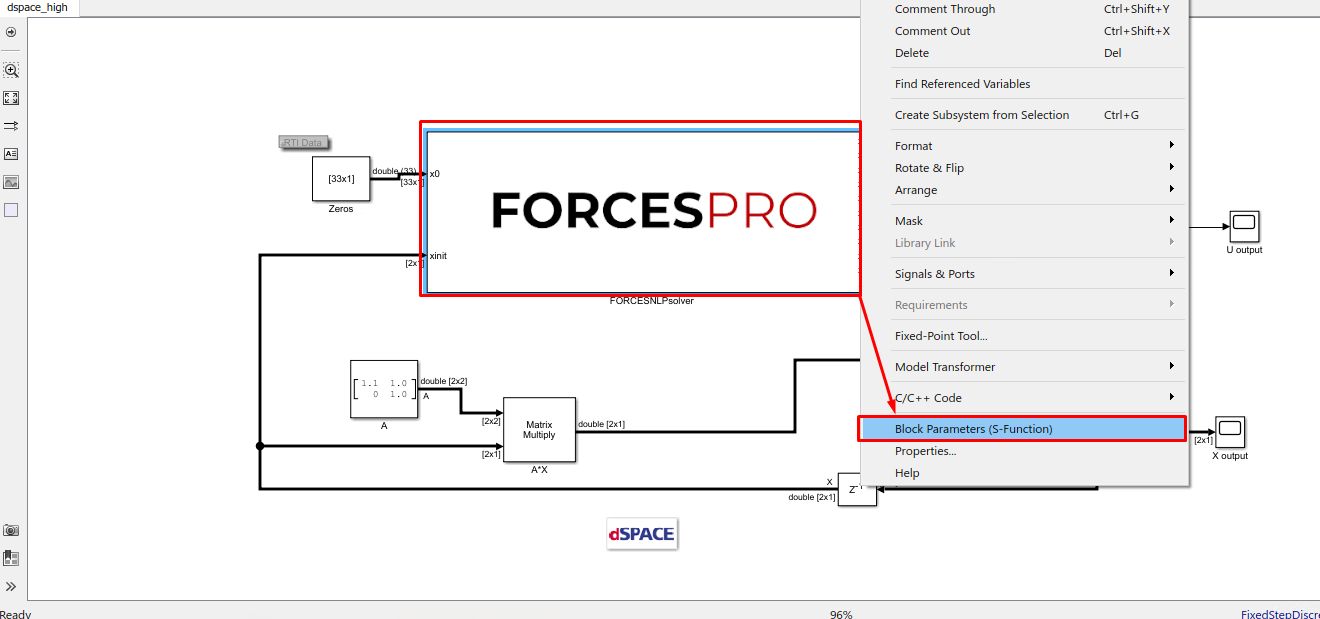
Figure 14.13 Open the FORCESPRO block’s parameters.¶
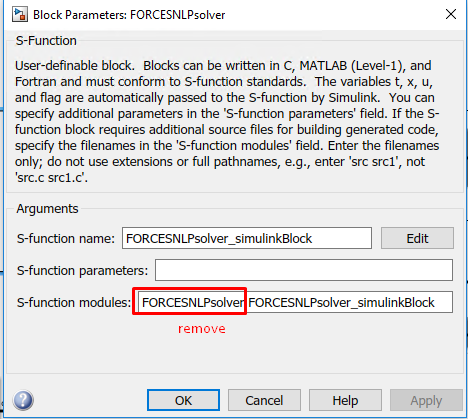
Figure 14.14 Remove the leading solver name from the S-function module.¶
Deployment is complete and simulations can now be run on the dSPACE platform.
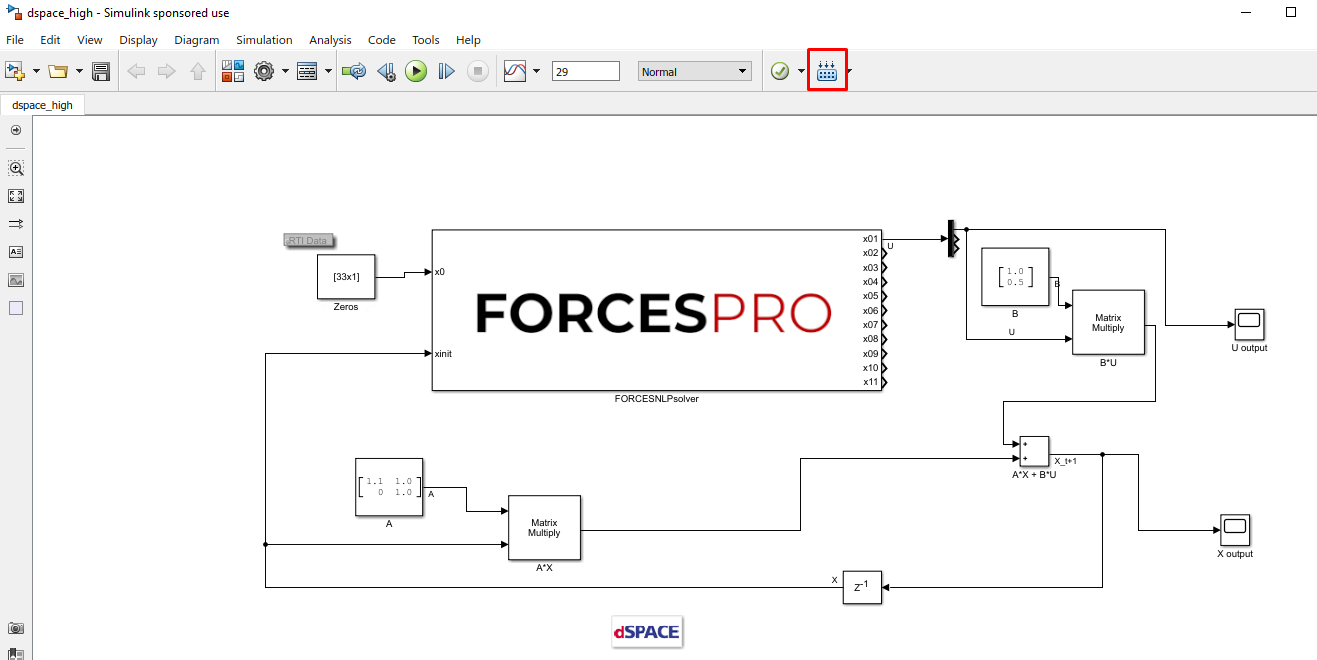
Figure 14.15 Compile the code of the Simulink model.¶
14.2.3. Y2F interface¶
14.2.3.1. Instructions¶
The steps to deploy and simulate a FORCESPRO controller on a dSPACE platform are detailed below.
(Figure 14.16) Set the code generation options (for
<platform_name>see Platform name codeoption):
codeoptions.platform = '<platform_name>'; % to specify the platform
codeoptions.printlevel = 0; % on some platforms printing is not supported
and then generate the code for your solver (henceforth referred to as “simplempc_solver”, placed in the folder “Y2F”) using the Y2F interface.
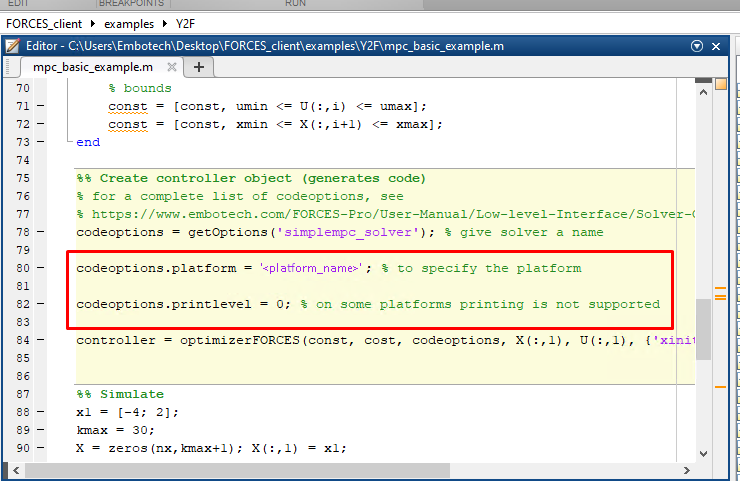
Figure 14.16 Set the appropriate code generation options.¶
(Figure 14.17) Create a new Simulink model using the Simulink model template provided by dSPACE (for
<simulink_model_template>see Simulink Model HW Target Configuration).(Figure 14.18) Populate the Simulink model with the system you want to control.
Figure 14.17 Create a Simulink model.¶
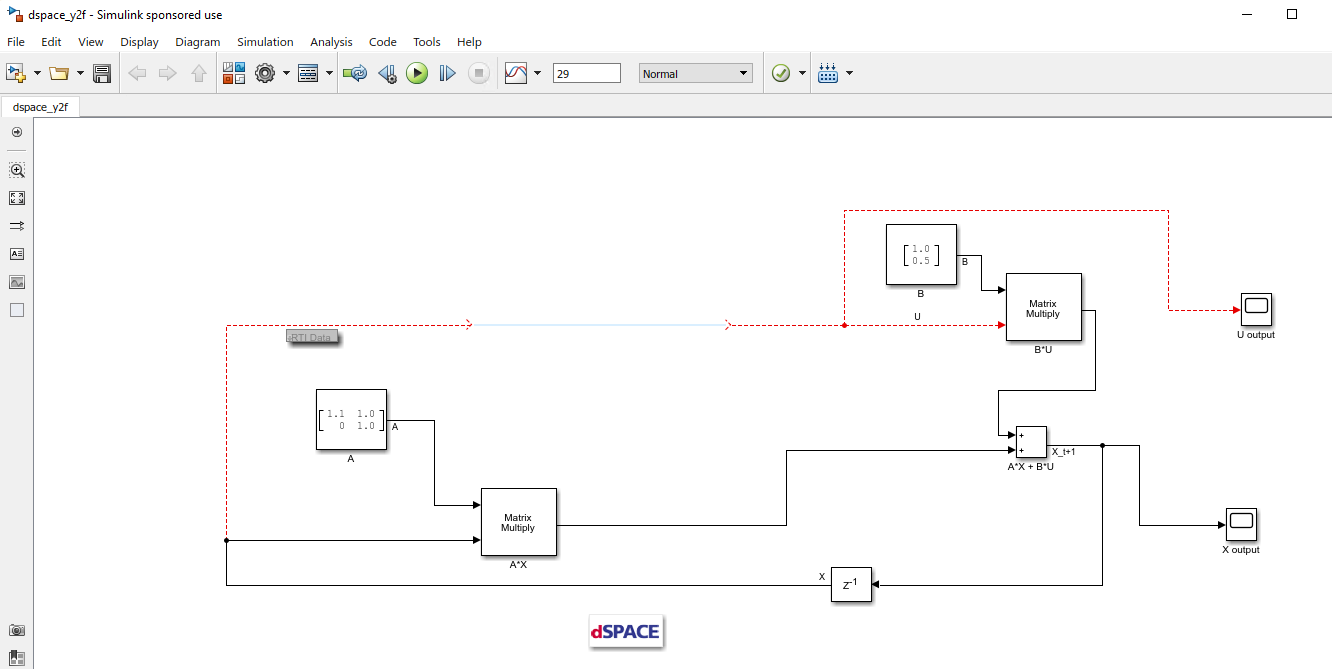
Figure 14.18 Populate the Simulink model.¶
(Figure 14.19) Make sure the
simplempc_solver_simulinkBlock.mexw64file (created during code generation) is on the MATLAB path.
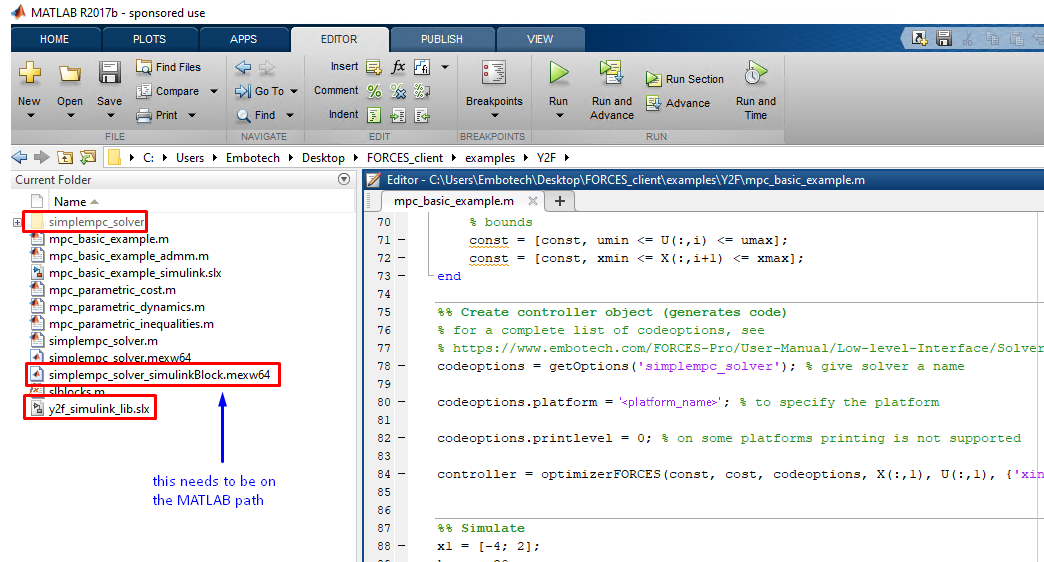
Figure 14.19 Add the folder containing the .mexw64 solver file to the MATLAB path.¶
(Figure 14.20) Copy-paste the FORCESPRO Simulink block, contained in the created
y2f_simulink_lib.slxSimulink model file, into your simulation model and connect its inputs and outputs appropriately.
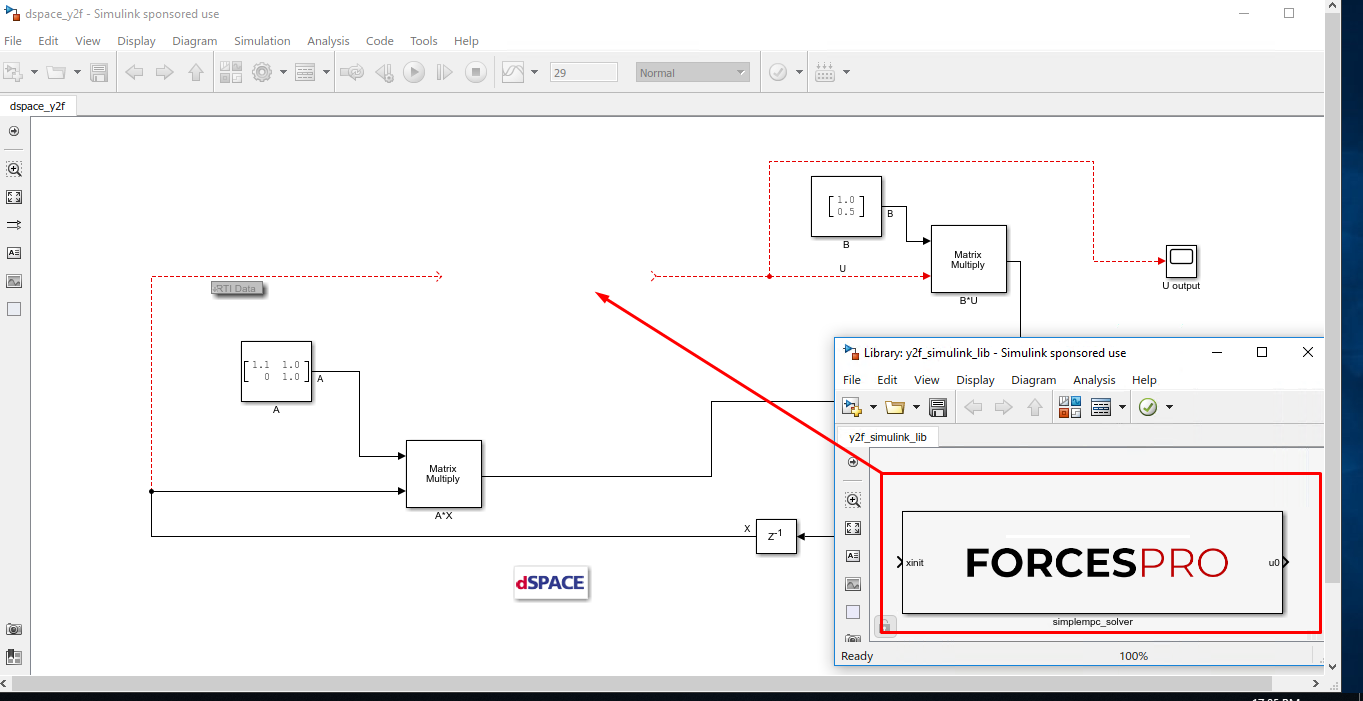
Figure 14.20 Copy-paste and connect the FORCESPRO block.¶
(Figure 14.21) Access the Simulink model’s options.
(Figure 14.22) In the “Solver” tab, set the options:
Simulation start/stop time: Depending on the simulation wanted.
Solver type: Discrete or fixed-step.
Fixed-step size: Needs to be higher than the execution time of the solver.
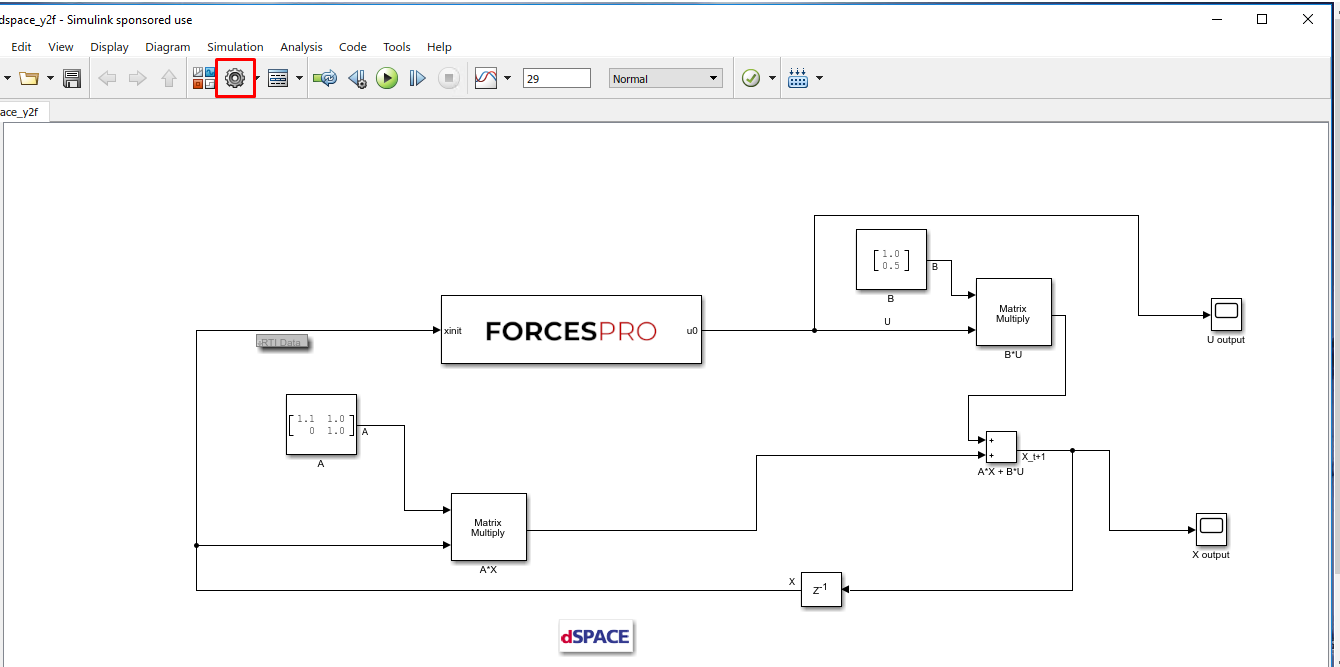
Figure 14.21 Open the Simulink model options.¶
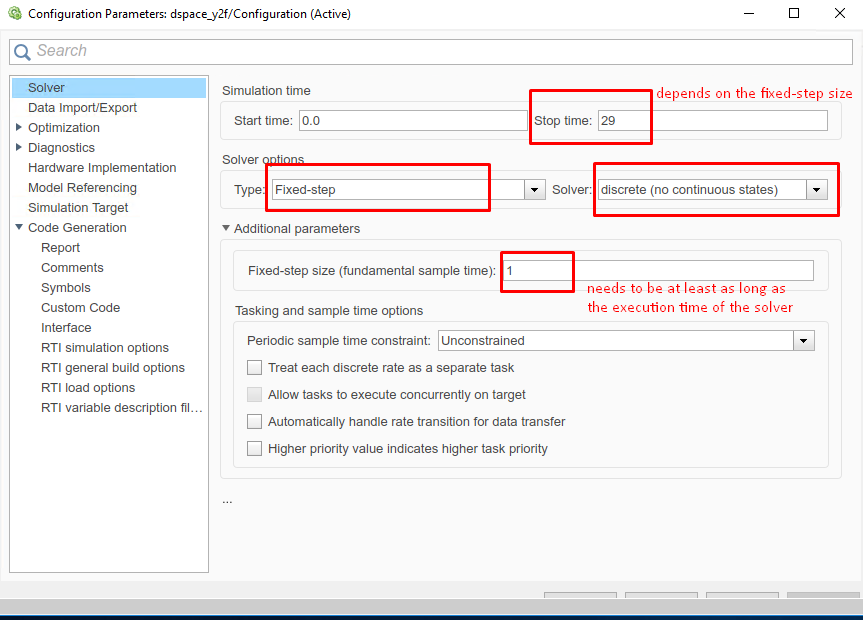
Figure 14.22 Set the Simulink solver options.¶
(Figure 14.23) In the “Code Generation/RTI general build options” tab, set the options (for
<tlc_file>and<makefile_template>see Simulink Model HW Target Configuration):System target file:
<tlc_file>Language: C
Generate makefile: On
Template makefile:
<makefile_template>Make command:
make_rti
(Figure 14.24) In the “Code Generation/Custom Code” tab, include the directories:
Y2F
Y2F\simplempc_solver\interface
Y2F\simplempc_solver\lib_target
(Figure 14.25) In the “Code Generation/Custom Code” tab, add the source files:
simplempc_solver_simulinkBlock.c
simplempc_solver.c
(Figure 14.26) In the “Code Generation/Custom Code” tab, add the library files:
i_simplempc_solver_1.lib
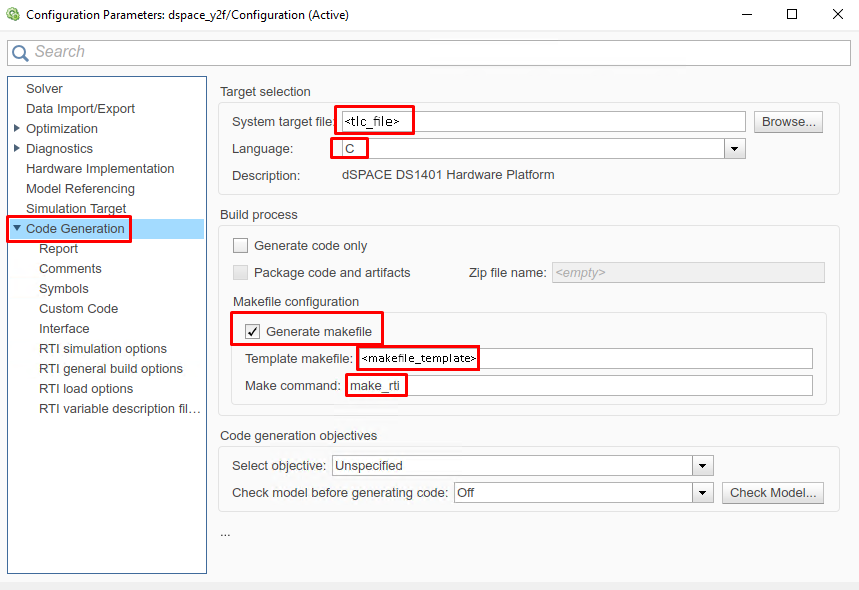
Figure 14.23 Set the Simulink code generation options.¶
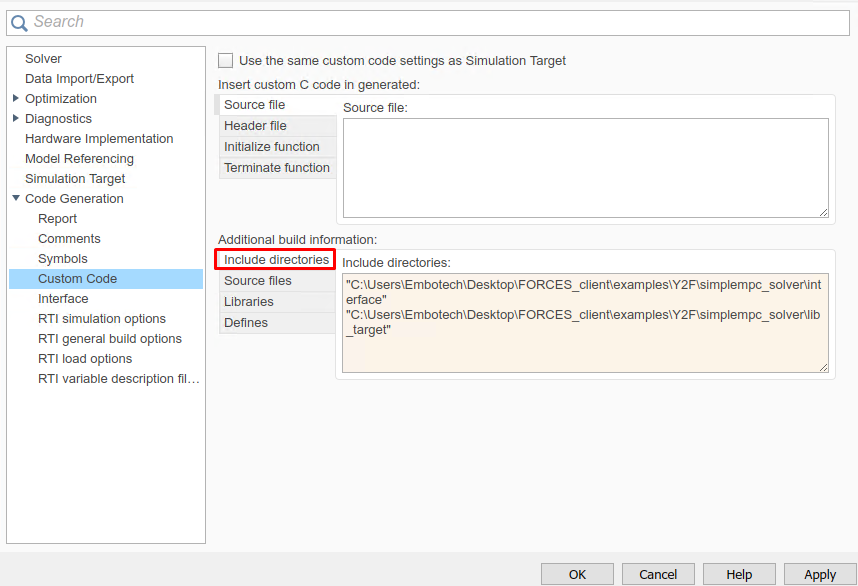
Figure 14.24 Add the directories included for the code generation.¶
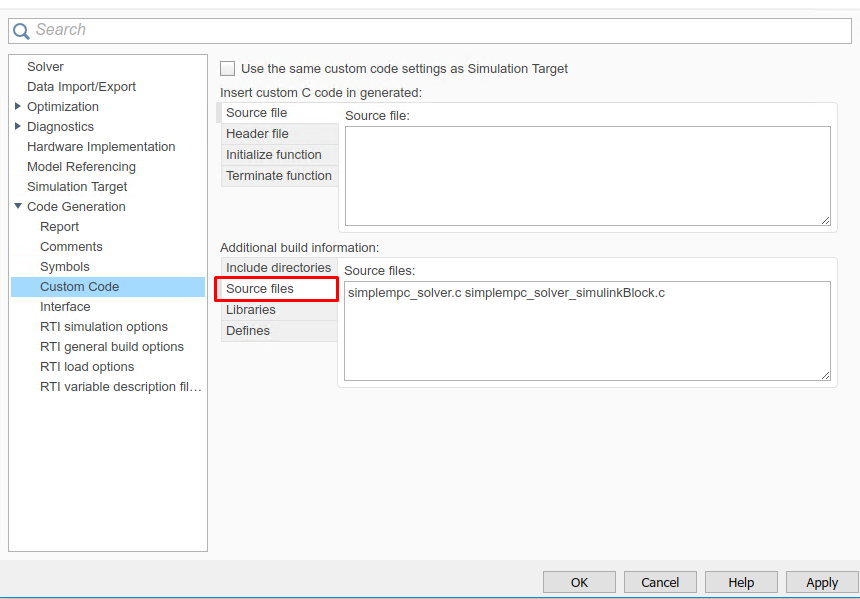
Figure 14.25 Add the source files used for the code generation.¶
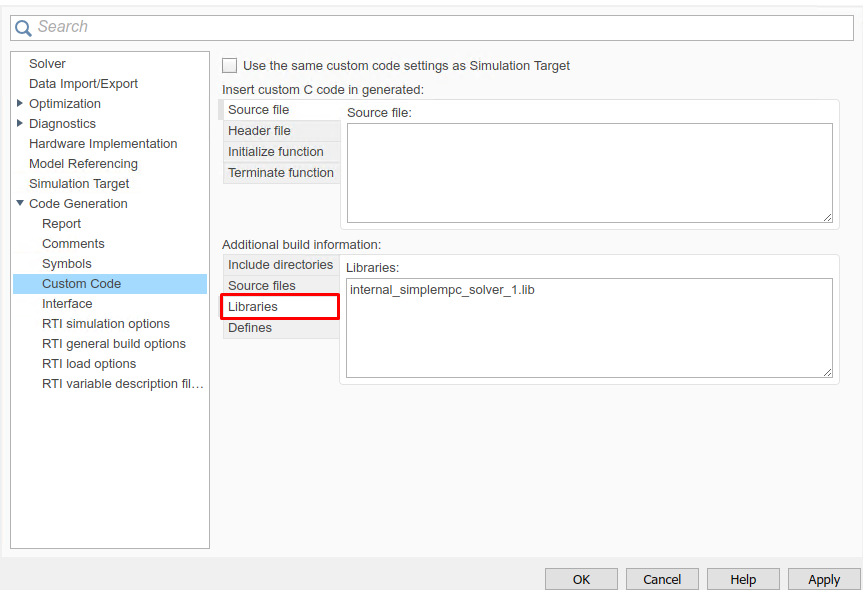
Figure 14.26 Add the libraries used for the code generation.¶
(Figure 14.27) Compile the code of the Simulink model. This will also automatically load the model to the connected dSPACE platform.
Deployment is complete and simulations can now be run on the dSPACE platform.
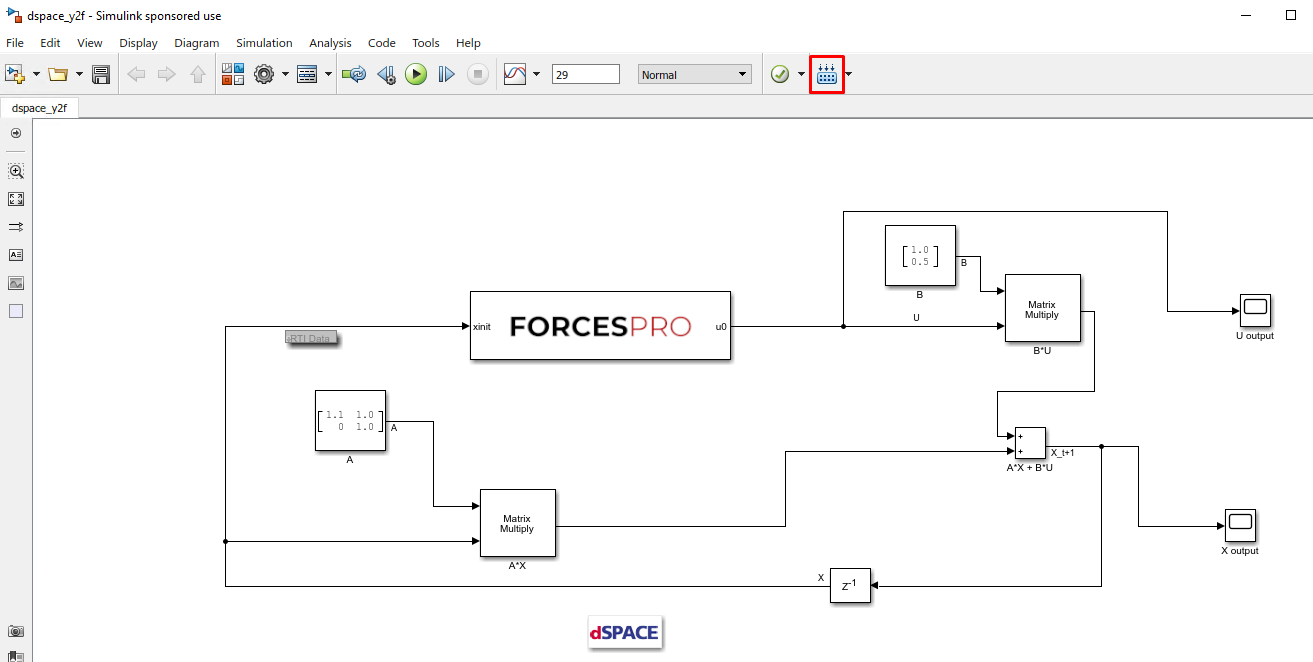
Figure 14.27 Compile the code of the Simulink model.¶